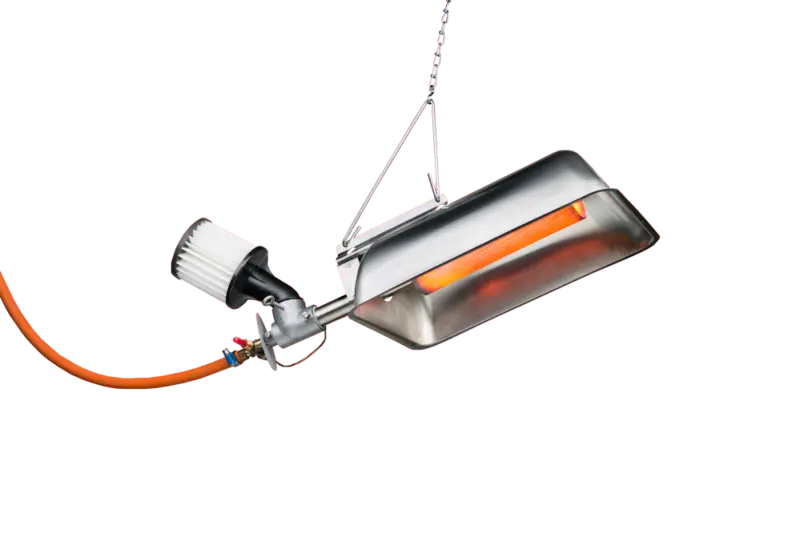
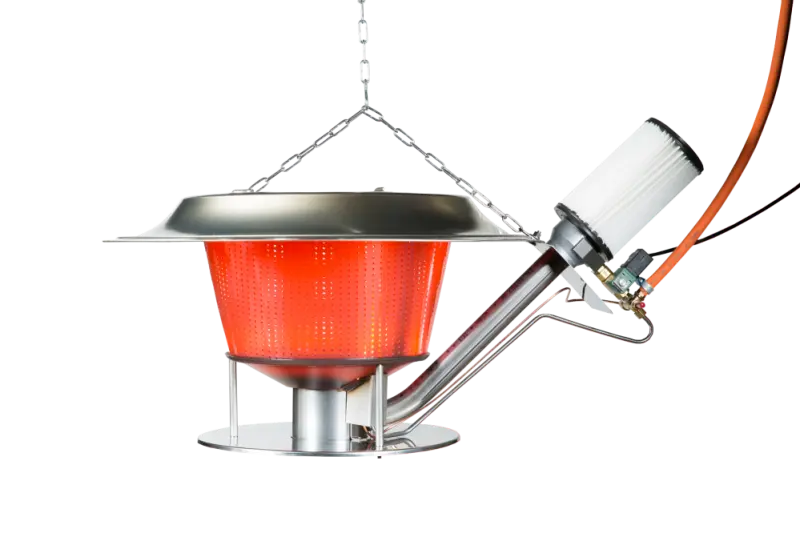
Infrared heating
As close to nature as heating can be
Anyone sitting in the sun knows that the sun gives extra heat and an extra comfortable feeling although the temperature may not be high enough. Every time a cloud passes in front of the sun we are reminded of this. For animals sitting under a Gasolec Infrared Gas Heater is like sitting under the sun, as close to nature as heating can be.
In general there are three ways of transferring heat:
- Conduction
This is heat transportation within a solid material, metals in general are good conductors.- Convection
Using a medium that heats up (liquids, air, etc.) and than transferring the medium.- Radiation
Using a source which radiates its heat directly. The sun is a good example.
In practice all heating systems use all three principles of transferring the heat but there are big differences in the ratios between these three variables between the systems. At Gasolec our first priority has always been on Radiation Heat, to create artificial suns. The following is to give the reader some understanding of differences between these principles.
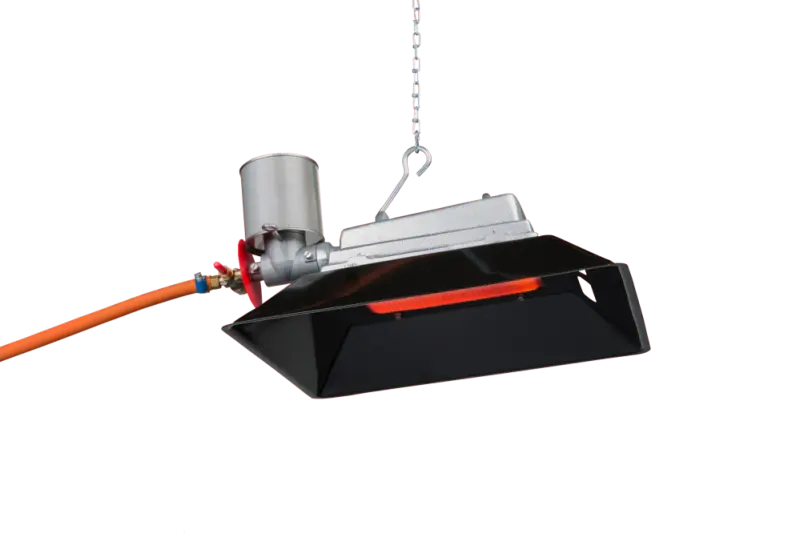

From the start Gasolec aimed for heating with Infrared Radiant Gas Heaters that produce a high ratio of Infrared radiation, a mini artificial sun.
Read more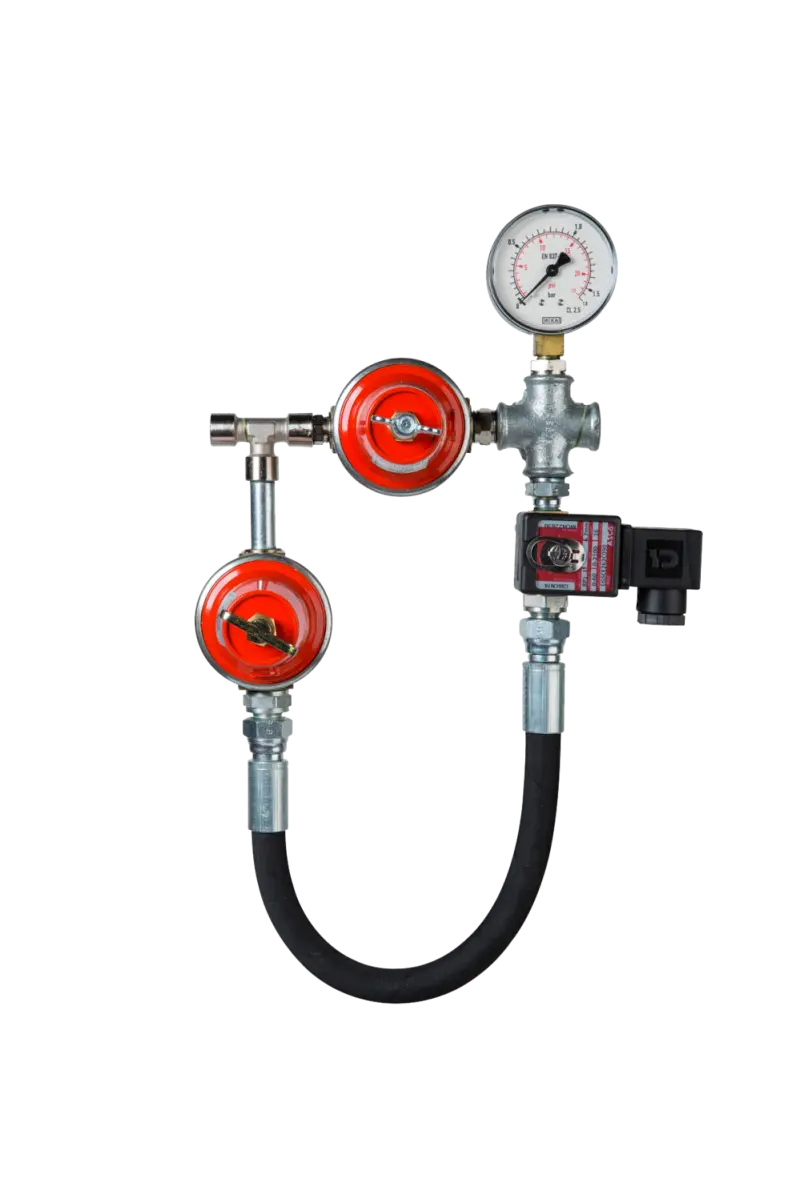
The function of Gas Pressure Regulators is to reduce the pressure of the gas that is available to the gas pressure required by the heater and by the heating controller. The gas supplied to a gas pressure regulator comes in different, sometimes fluctuating pressures. Just as...
Read more
Different gas cylinder connectors – also known as gas bottle connectors – are being used in various countries all over the world!
Read moreConduction:
Conduction heating is generally used for transporting heat over short distances and for that reason not suitable for heating large buildings like poultry houses.
Convection:
This is heating by moving warmer air or liquid to colder areas and thereby warming that area or spot one wants to warm. Hot air heating is a much used example in poultry houses. Typical of convection heating is that the heat always wants to go up first. This means that before one can heat the floor and the animals on the floor one has to heat the top of a room. This explains why in general preheating a poultry house with hot air heaters takes longer than preheating with Infrared Radiation heating.
Another characteristic of using convection heating with hot air units is that it can only work IF the air is moved around the poultry house with a certain speed, something small chicken don’t always appreciate.
Warm water is also often used as a transportation medium to distribute warmth, this is convection. By installing warm water lines in the floor of a poultry or pig house, these warm water lines then warm the floor around and above them through conduction. Another option is working with radiators that warm the air around them and by moving the air one can spread the heat. Both systems work but they require large investments and their efficiency is strongly depended on the insulation of the animal houses.
Radiation:
With radiation one can aim a large part of the heat output towards the place one wants to heat. The Gasolec Infrared Radiant Gas Heaters are designed to aim their output as much as possible downwards to heat the animals as well as the litter. With Infrared Radiation Heating one is less depended on the insulation of the animal houses as a big part of the heat is aimed towards the animals & the floor first. Of course good insulation always helps to reduce heating costs and we recommend our customers to insulate their animal houses properly. The infrared radiation reaches the things it should heat without air movement for a greater wellness of the animals. And as the litter is being warmed up by the radiation, it creates comfort zones where any animal can make its own choice as to where it prefers to stay!
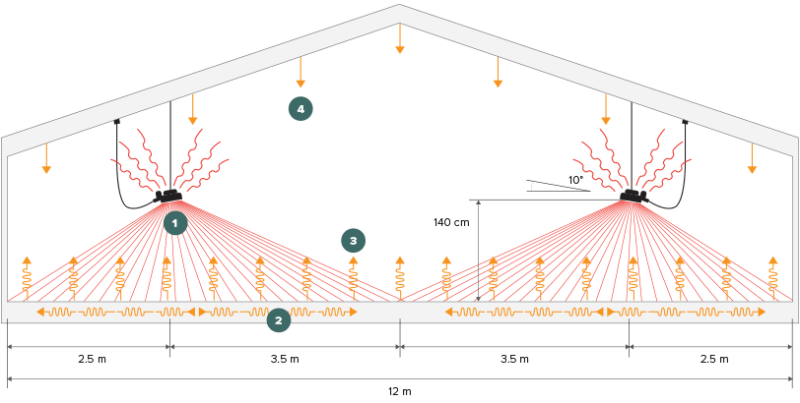
- 1 - Direct infrared heat from heaters to the floor
- 2 - Horizontal heat conduction within the floor
- 3 - Indirect radiant heat and convection upward from heated floor
- 4 - Indirect radiant heat and convection flow downward from ceiling
Creating Comfort zones
The idea behind comfort zones is that some animals like it a little warmer than others. Fact is that high performing animals in general produce more heat themselves so they need less extra heating. At the same time animals that don’t feel well, like to move towards a heat source. As shown in the above drawing, the further one is away from the heater, the temperature drops a little.
The drawings below show the heat distribution of a G12 heater from above.
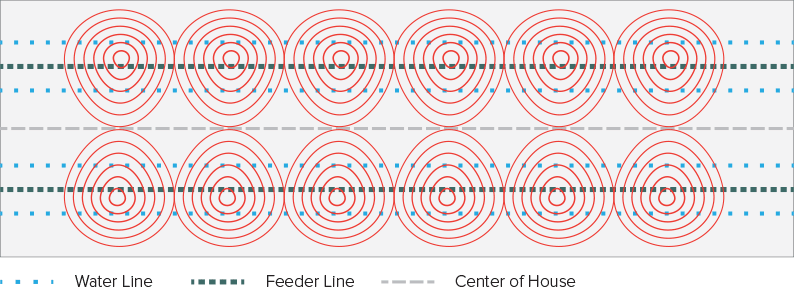
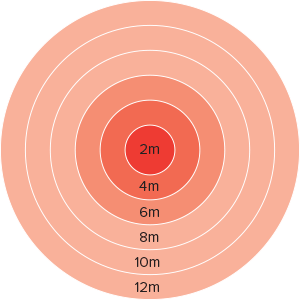
| Diameter | Ambient temperature | Temp of 1x G12 * |
|---|---|---|
| 2m | 17°C | 33°C |
| 4m | 17°C | 26°C |
| 6m | 17°C | 23°C |
| 8m | 17°C | 21°C |
| 10m | 17°C | 21°C |
| 12m | 17°C | 21°C |
* After 30 min. heating measured on the floor with a G12 heater